4 types of Marketing Information Systems: An In-Depth Exploration
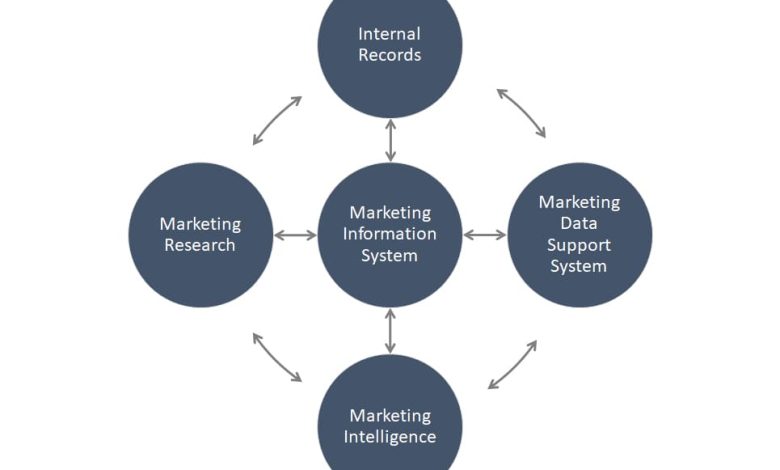
In the contemporary business landscape, effective decision-making is crucial for the success of any organization. One of the key ways organizations can enhance their decision-making is through the use of Marketing Information Systems (MIS). These systems serve as a foundation for capturing, analyzing, and disseminating relevant marketing information, enabling businesses to devise informed strategies that align with their objectives. This article will delve into the four main types of marketing information systems: Internal Databases, Marketing Intelligence Systems, Marketing Research Systems, and Decision Support Systems. Additionally, we will explore how each type can benefit organizations across various aspects of their operations.
1. Internal Databases
Definition and Components
Internal databases are repositories that store a company’s information accumulated from various internal sources. This data can include sales records, customer interactions, financial transactions, and more. Internal databases can be divided into several components, including:
- Customer Databases: Information about customers’ demographics, preferences, purchasing patterns, and feedback.
- Sales Data: Historical sales information that helps in forecasting and trend analysis.
- Product Information: Data regarding stock, pricing, and performance of various products.
- Marketing Campaign Data: Results and analyses of past and present marketing initiatives.
Benefits to Organizations
- Enhanced Customer Understanding: Internal databases provide organizations with a wealth of information regarding their customers. By analyzing this data, businesses can better understand customer needs and preferences, allowing for more personalized marketing efforts.
- Improved Operational Efficiency: Access to detailed sales and inventory data enables companies to streamline operations. Businesses can improve stock management, reduce waste, and optimize pricing strategies based on historical performance.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Decision-making is significantly improved when organizations rely on actual data rather than assumptions or gut feelings. Internal databases foster a culture of data-driven decision-making, ensuring that marketing, sales, and product development efforts are grounded in reality.
- Increased Retention Rates: By analyzing customer behavior patterns, companies can develop targeted marketing strategies to enhance customer retention. Internal databases enable businesses to identify at-risk customers and implement retention campaigns that resonate with them.
- Performance Tracking: Organizations can monitor the success of their marketing campaigns through sales data found in internal databases. By analyzing metrics such as ROI (Return on Investment), businesses can make adjustments to strategies in real-time.
2. Marketing Intelligence Systems
Definition and Components
Marketing Intelligence Systems (MIS) involve the systematic collection and analysis of publicly available information regarding the market, competitors, and overall industry trends. These systems encompass various data sources, including:
- Public Records: Information derived from government reports, financial statements, and industry publications.
- Competitor Analysis: Data regarding competitors’ marketing strategies, pricing, and product offerings.
- Market Trends: Insights and forecasts regarding new market developments, consumer behavior shifts, and economic indicators.
Benefits to Organizations
- Competitive Advantage: By staying informed about competitors’ moves and market trends, organizations can adapt their strategies accordingly. Marketing intelligence helps businesses stay ahead of the competition by anticipating market shifts and consumer needs.
- Proactive Decision-Making: Marketing intelligence allows businesses to make proactive rather than reactive decisions. Organizations that monitor market trends can identify opportunities for product development, new market entry, and other strategic initiatives.
- Risk Reduction: With access to comprehensive market data, organizations can minimize risks associated with launching new products or entering new markets. Understanding potential challenges and competitors provides organizations with the ability to make informed choices.
- Strategic Positioning: By leveraging marketing intelligence, organizations can enhance their market positioning. They can identify unmet needs in the market and tailor their value propositions accordingly, leading to better-targeted marketing campaigns.
- Enhanced Innovation: Insights gleaned from marketing intelligence systems encourage innovation. Businesses that understand emerging trends and consumer preferences can foster creativity in product development and marketing approaches.
3. Marketing Research Systems
Definition and Components
Marketing Research Systems involve the systematic collection, analysis, and interpretation of data related to marketing activities. These systems gather qualitative and quantitative data through various research methods, including:
- Surveys and Questionnaires: Tools designed to gather direct feedback from customers and prospects about their preferences and satisfaction.
- Focus Groups: In-depth discussions with selected groups of individuals aimed at exploring attitudes and perceptions towards products or brands.
- Observational Research: Gathering data by observing consumer behaviors in natural settings or controlled environments.
Benefits to Organizations
- Informed Product Development: Marketing research systems allow organizations to gather consumer insights before launching new products or features. This reduces the likelihood of product failure and enhances the chances of market acceptance.
- Target Audience Identification: Conducting targeted research helps organizations define and segment their market effectively. With a clearer understanding of demographics, psychographics, and behavior, businesses can tailor marketing messages to resonate with specific groups.
- Measuring Brand Health: Marketing research helps companies assess brand equity and overall perception among consumers. This information allows organizations to make adjustments in positioning and messaging to strengthen brand loyalty.
- Adaptation to Market Changes: In today’s fast-paced environment, consumer preferences can shift rapidly. Marketing research systems enable organizations to stay attuned to these changes and adapt their offerings and strategies in real time.
- Validation of Marketing Strategies: Organizations can test different marketing strategies and tactics through research. By measuring the effectiveness of various approaches, businesses can continuously refine their marketing efforts for optimal performance.
4. Decision Support Systems (DSS)
Definition and Components
Decision Support Systems in marketing consist of computer-based tools that help managers make informed decisions based on data analysis. These systems often integrate information from internal databases, marketing intelligence, and research, and may include features such as:
- Data Analysis Tools: Software applications that assist in data interpretation and visualization to support decision-making processes.
- Simulation Models: Scenarios that simulate the outcomes of different marketing strategies based on varying inputs, providing insights into potential results.
- Reporting Functions: Automated reporting features that deliver relevant information to stakeholders, facilitating timely decision-making.
Benefits to Organizations
- Streamlined Decision-Making Process: Decision Support Systems expedite the decision-making process by providing timely and relevant data. Managers can access insights quickly, enabling them to act promptly in dynamic market environments.
- Comprehensive Analysis: DSS tools facilitate comprehensive analysis by combining data from various sources. This holistic view enables organizations to understand complex scenarios and make decisions that consider multiple factors.
- Scenario Planning: By utilizing simulation models, organizations can explore various “what-if” scenarios. This capability allows decision-makers to assess the potential impact of different strategies before committing resources.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Decision Support Systems often integrate collaborative features that allow team members to contribute to the decision-making process. This enhances the quality of decisions as multiple perspectives are considered.
- Performance Monitoring: DSS tools provide metrics and KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) that help organizations monitor the outcomes of their decisions. Continuous assessment leads to informed adjustments and enhanced marketing effectiveness.
Conclusion
The integration of Marketing Information Systems into an organization’s operations can unlock unparalleled potential for growth and efficiency. Each type—Internal Databases, Marketing Intelligence Systems, Marketing Research Systems, and Decision Support Systems—offers unique advantages and, when employed collectively, they create a robust framework for understanding and responding to market dynamics effectively.
Organizations that leverage these systems position themselves to:
- Gain a deeper understanding of their customers’ needs and behaviors.
- Stay informed about competitive landscapes and market trends.
- Ground their marketing strategies in research-backed insights.
- Enhance decision-making processes with data-driven tools.
In an era characterized by rapid technological advancements and evolving consumer expectations, investing in a well-rounded Marketing Information System is not just beneficial; it is essential for long-term success and sustainability in the marketplace. By embracing these systems, organizations can future-proof their marketing efforts, adapt strategies to changing environments, and ultimately achieve their business objectives more effectively.





2 Comments